If some salt is added to the water, it will dissociate into positive and negative ions. Negative ions will gather around positively charged colloidal particles while positive ions will be repelled. This way the electric field of the colloidal particle will be screened. If enough salt is added, the colloid will precipitate out. (This is called salting out a colloid.)
Find the electric potential around a colloidal particle! Consider the concentration of positive and negative ions to be the same n0 far away from the particle. You will need the formula for the Boltzmann-distribution: particles in a potential are distributed in such a way that the number of particles having potential energy E is proportional to e-E∕kT . For this calculation consider the case when kT ≫ E.
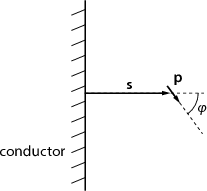
 ) is situated at distance s from an infinite conducting
sheet. The angle between
) is situated at distance s from an infinite conducting
sheet. The angle between 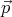 and the sheet’s normal is φ. Find the torque
acting on the dipole! What orientation will the dipole adopt if it is allowed
to rotate freely, but its distance from the sheet is kept constant?
and the sheet’s normal is φ. Find the torque
acting on the dipole! What orientation will the dipole adopt if it is allowed
to rotate freely, but its distance from the sheet is kept constant?
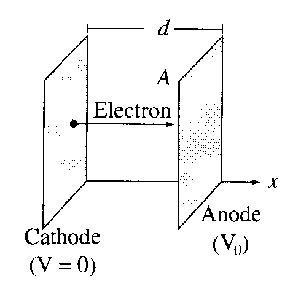
|
Suppose the plates are large relative to the separation, so that edge effects can be neglected. Then V , ρ, and v (the speed of electrons) are all functions of x alone.
- Find V,ρ, and v as a functions of x.
- Show that I = KV 03∕2, and find the constant K. This equation is called the Child–Langmuir law. It holds for other geometries as well, whenever space-charge limits the current. Notice that the space-charge limited diode does not obey Ohm’s law!
If you need hints, you will find the detailed steps to reach the solution in the book by Griffihts, problem 2.48.